Optimal headrest height for the best laryngoscopic view: by anatomical measurements
Affiliations
- Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, 166, Gumi-ro, Seongnam City, Kyeonggi-do, 463-802, Korea
Affiliations
- Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, 166, Gumi-ro, Seongnam City, Kyeonggi-do, 463-802, Korea
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, 166, Gumi-ro, Seongnam City, Kyeonggi-do, 463-802, Korea
Affiliations
- Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, 166, Gumi-ro, Seongnam City, Kyeonggi-do, 463-802, Korea
Affiliations
- Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, 28, Yongon-Dong, Jongno-gu, Seoul
Affiliations
- Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, 166, Gumi-ro, Seongnam City, Kyeonggi-do, 463-802, Korea
Correspondence
- Corresponding author. Department of Anesthesiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, 166 Gumi-ro, Seongnam City, Kyeonggi-do, 463-802, Korea. Tel.: +82 31 787 7494; fax: +82 31 787 4063.

Affiliations
- Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, 166, Gumi-ro, Seongnam City, Kyeonggi-do, 463-802, Korea
Correspondence
- Corresponding author. Department of Anesthesiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, 166 Gumi-ro, Seongnam City, Kyeonggi-do, 463-802, Korea. Tel.: +82 31 787 7494; fax: +82 31 787 4063.
 Article Info
Article Info
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
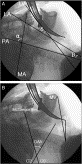
Fig. 1
A, Lateral radiograph of the head and neck taken at the best laryngoscopic view with a no. 3 Macintosh curved blade (MCB) displaying the four axes (mouth axis [MA], pharyngeal axis [PA], laryngeal axis [LA], line of vision [LV]) and the α, β, and δ angles. B, Larynx visualization space (intubation distance = ID) from C5 to MCB tip marked. Mentovertebral distance (MV) from C5 to mentum to measure anterior displacement of the jaw during laryngoscopy. The McGregor line, which connects the most dorsal edge of and caudal portion of the occiput and the dorsal edge of the hard palate, is used as reference for the occiput (C0). A reference line for the axis (C2) is drawn through the basal plate of the vertebral body. The occipito-atlanto-axial (OAA) extension angle between C0 and C2 is measured.
Abstract
Background
We hypothesized that the oro-pharyngolaryngeal axes, occipito-atlanto-axial extension (OAA) angle and intubation distance would be influenced by the height of headrests.
Methods
Twenty patients were enrolled. The Macintosh 3 blade was used for direct laryngoscopy without a headrest or with the headrest of 6 or 12 cm high in randomized order, whereas a lateral radiograph of the neck was taken when the best laryngoscopic view was obtained. The following measurements were made: (1) the axis of the mouth (MA), the pharyngeal axis (PA), the laryngeal axis (LA), and the line of vision (LV). The various angles between these axes were defined: α angle between MA and PA, β angle between PA and LA, and δ angle between LV and LA. (2) Intubation distance, (3) mentovertebral distance, and (4) OAA angle.
Results
Compared with 12-cm and no headrest, the δ angle decreased significantly with 6-cm headrest (19.4°/29.2°/29.2° in 6-cm/12-cm/no headrest, respectively; P < .001), and the intubation distance increased significantly (46.2/37.3/38.7 mm in 6-cm/12-cm/no headrest, respectively; P < .001). Mentovertebral distance was smallest (107.0/106.7/98.5 mm; P < .05) at 12-cm headrest. Occipito-atlanto-axial extension angle was largest significantly (40.7°/35.2°/34.5°; P < .05) at 6-cm headrest.
Conclusion
We conclude that compared with no or 12-cm headrest, 6-cm headrest could facilitate more alignment of these axes, increase the OAA angle, and enlarge the intubation distance.
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..


