Short- and long-term cardiac events in patients with chest pain with or without known existing coronary disease presenting normal electrocardiogram
Affiliations
- Emergency Medicine, Department of Critical Care Medicine and Surgery, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
Correspondence
- Corresponding author. Emergency Medicine Department, Careggi University Hospital and Department of Critical Care Medicine and Surgery, University of Florence, Florence, Italy.

Affiliations
- Emergency Medicine, Department of Critical Care Medicine and Surgery, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
Correspondence
- Corresponding author. Emergency Medicine Department, Careggi University Hospital and Department of Critical Care Medicine and Surgery, University of Florence, Florence, Italy.
Affiliations
- Emergency Medicine, Department of Critical Care Medicine and Surgery, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
Affiliations
- Emergency Medicine, Department of Critical Care Medicine and Surgery, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
Affiliations
- Emergency Medicine, Department of Critical Care Medicine and Surgery, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
Affiliations
- Emergency Medicine, Department of Critical Care Medicine and Surgery, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
Affiliations
- Emergency Medicine, Department of Critical Care Medicine and Surgery, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
Affiliations
- Emergency Medicine, Department of Critical Care Medicine and Surgery, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
Affiliations
- Emergency Medicine, Department of Critical Care Medicine and Surgery, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
Affiliations
- Department of Cardiology, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
Affiliations
- Department of Cardiology, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
 Article Info
Article Info
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
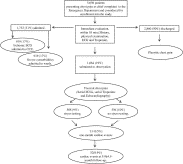
Fig. 1
Flow diagram of management in patients with chest pain presenting to the ED (n = 5656). End point: cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, unstable angina, and revascularization at short-term (1 month) and long-term (9.9 ± 4.9 months) follow-up.
Fig. 2
Flow diagram of patients with known coronary disease enrolled in the study (n = 477). End point: cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, unstable angina, and revascularization during in-hospital stay, at short-term (1 month) and long-term (9.9 ± 4.9 months) follow-up.
Fig. 3
Flow diagram of patients without known coronary disease enrolled in the study (n = 587). End point: cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, unstable angina, and revascularization during in-hospital stay, at short-term (1 month) and long-term (9.9 ± 4.9 months) follow-up.
Abstract
Aim
The aim of this study is to evaluate incidence of adverse cardiac events in patients with chest pain with or without known existing coronary disease presenting normal electrocardiogram (ECG) and initial troponin.
Methods
Prospective, nonrandomized study enrolled low-risk patients with normal ECG and troponin on admission who underwent observation and/or stress testing by unstandardized clinical judgment. Patients who experienced recurrent angina or positive ECGs or positive troponins during observation or patients with positive stress testing were admitted; otherwise, they were discharged.
End Point
The end points are cardiac events at short- and long-term follow-up including cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, unstable angina, and revascularization.
Results
Of 5656 patients considered, 1732 with ischemic ECG were initially admitted and, therefore, excluded from the analysis; 2860 with pleuritic chest pain and normal ECG were discharged; 1064 with visceral chest pain and normal ECG were enrolled. Patients with known coronary disease (45%) were older and likely presented known vascular disease. Patients with known vascular disease, older age, female sex, diabetes mellitus, and lower chest pain score were likely managed with observation. In patients with known coronary disease as compared with patients without, overall cardiac events account for 35% vs 14%, respectively (P < .001), as follows: in-hospital, 23% vs 10%, (P < .001); 1 month, 4% vs 2% (P = .133); and 9.9 ± 4.9 months, 8% vs 2%, respectively (P < .001).
Conclusions
One-third of patients with chest pain with known coronary disease, negative ECG, and biomarkers were subsequently found to have adverse cardiac events. The value of this research for an emergency medicine audience could be extended to all clinicians and general practitioners beyond cardiologists.
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..


