Passive leg raising during cardiopulmonary resuscitation results in improved neurological outcome in a swine model of prolonged ventricular fibrillation☆☆☆
Affiliations
- Department of Anatomy, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Medical School, Athens, Greece
Affiliations
- 2nd Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Medical School, Aretaieion Hospital, Athens, Greece
Affiliations
- Department of Anatomy, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Medical School, Athens, Greece
Correspondence
- Corresponding author. Tel.: +30 2104133992; fax: +30 2107462305.

Affiliations
- Department of Anatomy, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Medical School, Athens, Greece
Correspondence
- Corresponding author. Tel.: +30 2104133992; fax: +30 2107462305.
Affiliations
- National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Medical School, Laboratory for Musculoskeletal Research, KAT Hospital, Athens, Greece
Affiliations
- Department of Internal Medicine, General Hospital of Ierapetra, Crete, Greece
Affiliations
- Experimental-Research Center “ELPEN” Pharmaceutical Co, Athens, Greece
Affiliations
- Department of Anatomy, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Medical School, Athens, Greece
 Article Info
Article Info
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
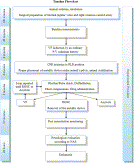
Fig. 1
Timeline flowchart of experimental protocol. NAS = Neurological Alertness Score.
Fig. 2
Coronary perfusion pressure fluctuation during the experimental procedure. Numbers above mean values indicate animals with ROSC at next rhythm check, and numbers in parenthesis indicate the total number of animals with ROSC at next rhythm check. BL = baseline.
Fig. 3
End-tidal CO2 fluctuations during the experimental procedure. No significant differences were observed during CPR. Numbers above mean values indicate animals with ROSC at next rhythm check, and numbers in parenthesis indicate the total number of animals that achieved ROSC at next rhythm check.
Abstract
Objective
The objective was to evaluate whether passive leg raising during cardiopulmonary resuscitation in a porcine model of prolonged ventricular fibrillation improves hemodynamics, return of spontaneous circulation, 24-hour survival, and neurological outcome.
Methods
Ventricular fibrillation was induced in 20 healthy Landrace/Large White piglets, which were subsequently left untreated for 8 minutes. Ten animals were randomly assigned into the control group and were resuscitated according to the 2005 European Resuscitation Council guidelines, and 10 piglets were assigned into the passive leg raising group and were resuscitated with the legs passively raised at 45° with the aid of a special purpose-made metallic device. End points were either return of spontaneous circulation or asystole.
Results
Return of spontaneous circulation was observed in 6 and 9 animals from the control and the passive leg raising group, respectively (P = .121; odds ratio = 0.16; 95% confidence interval, 0.01-1.87). Just prior to the first defibrillation attempt, coronary perfusion pressure was significantly higher in the passive leg raising group (22.8 ± 9.5 vs 10.6 ± 6.5 mm Hg, P < .004); but no subsequent significant differences were observed. Although all animals that restored spontaneous circulation survived for 24 hours, neurologic alertness score was significantly better in the animals treated with passive leg raising (90 ± 10 vs 76.6 ± 12.1, P = .037).
Conclusions
Passive leg raising during cardiopulmonary resuscitation significantly increased coronary perfusion pressure in the minute prior to the first shock. Return of spontaneous circulation and 24-hour survival rate were comparable between groups. However, the animals in the passive leg raising group exhibited significantly higher neurological scores.
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
☆Funding sources: Experimental-Research Center “ELPEN” Pharmaceutical Co, Athens, Greece.
☆☆Conflict of interests: none.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..


