Clinical management of atrial fibrillation: early interventions, observation, and structured follow-up reduce hospitalizations
Affiliations
- Emergency Medicine, Department of Critical Care Medicine and Surgery, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
Correspondence
- Corresponding author.

Affiliations
- Emergency Medicine, Department of Critical Care Medicine and Surgery, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
Correspondence
- Corresponding author.
Affiliations
- Emergency Medicine, Department of Critical Care Medicine and Surgery, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
Affiliations
- Emergency Medicine, Department of Critical Care Medicine and Surgery, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
Affiliations
- Emergency Medicine, Department of Critical Care Medicine and Surgery, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
Affiliations
- Emergency Medicine, Department of Critical Care Medicine and Surgery, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
Affiliations
- Emergency Medicine, Department of Critical Care Medicine and Surgery, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
Affiliations
- Emergency Medicine, Department of Critical Care Medicine and Surgery, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
Affiliations
- Emergency Department, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
Affiliations
- Department of Cardiology, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
Affiliations
- Department of Cardiology, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy
 Article Info
Article Info
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
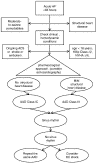
Fig. 1
The chart of time to treatment in patients presenting with AF lasting less than 48 hours. Class ADD, Vaughan-Williams class of antiarrhythmic drugs.
Fig. 2
Patients enrolled in groups 1, 2 and 3 (black bars); patients admitted (gray bars). *P < .001.
Fig. 3
Flow diagram of management of patients presenting with AF lasting less than 48 hours without structural heart disease and eligible for pharmacological conversion. Class IC AAD vs class III AAD, P < .001. Class ADD, Vaughan-Williams class of antiarrhythmic drugs.
Abstract
Background
Novel facilities such as an intensive observation unit and an outpatient clinic could result in improving management of patients presenting with atrial fibrillation (AF).
Methods
This observational study enrolled 3475 patients. Group 1 (1120 patients; years 2004-2005) was managed with standard approach; group 2 (992 patients; years 2006-2007) was managed with additional intensive observation; group 3 (1363 patients; years 2008-2009) was managed with additional intensive observation and outpatient clinic. Primary end point was admission to hospital. Secondary end points included modalities of rhythm conversion and administration of class IC vs class III antiarrhythmic drugs in patients with AF lasting less than 48 hours.
Results
Lack of rhythm control, comorbidities, diabetes, and age were independent predictors of hospitalization. Admissions significantly decreased from group 1 (50%) to 2 (38%) and to 3 (24%) (P < .001). Interestingly, more than a quarter of patients in group 3 were referred to the outpatient clinic for short-term follow-up, eventually avoiding admission. Patients with AF lasting less than 48 hours (n = 2189) and without structural heart disease (n = 1685) achieved sinus rhythm in 89% of cases and were discharged. In these patients, early administration of antiarrhythmic drugs of class IC and III gained sinus rhythm in 80% and 20%, respectively (P < .001). Spontaneous conversion occurred in 26%; electrical, 17%; and pharmacological, 57%.
Conclusions
In patients with AF, beyond the standard approach, the novel organization with an additional intensive observation unit for early pharmacological interventions and an outpatient clinic for elective treatment and short-term follow-up significantly reduced admission irrespective of independent predictors of hospitalizations. Patients without structural heart disease treated with antiarrhythmic drugs achieved sinus rhythm in 89% of cases, mostly with class IC drugs.
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..


