The first-door-to-balloon time delay in STEMI patients undergoing interhospital transfer☆
Affiliations
- Laboratory of Emergency Medical Service, Seoul National University Hospital Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul, Korea
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
Affiliations
- Laboratory of Emergency Medical Service, Seoul National University Hospital Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul, Korea
Correspondence
- Corresponding author at: Laboratory of Emergency Medical Service, Seoul National University Hospital Biomedical Research Institute, 28-2, Yeongeon-dong, Jongno-gu, Seoul 110-799, Korea. Tel.: +82 10 9152 5955; fax: +82 2 744 3967.

Affiliations
- Laboratory of Emergency Medical Service, Seoul National University Hospital Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul, Korea
Correspondence
- Corresponding author at: Laboratory of Emergency Medical Service, Seoul National University Hospital Biomedical Research Institute, 28-2, Yeongeon-dong, Jongno-gu, Seoul 110-799, Korea. Tel.: +82 10 9152 5955; fax: +82 2 744 3967.
Affiliations
- Laboratory of Emergency Medical Service, Seoul National University Hospital Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul, Korea
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
Affiliations
- Laboratory of Emergency Medical Service, Seoul National University Hospital Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul, Korea
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
Affiliations
- Laboratory of Emergency Medical Service, Seoul National University Hospital Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul, Korea
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Kyungpook National University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
Affiliations
- Laboratory of Emergency Medical Service, Seoul National University Hospital Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul, Korea
Affiliations
- Laboratory of Emergency Medical Service, Seoul National University Hospital Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul, Korea
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
 Article Info
Article Info
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
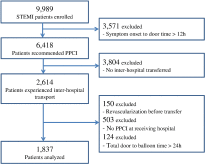
Fig. 1
Patient flow in the present study. PPCI, primary percutaneous coronary intervention.
Fig. 2
The 4 individual processes of care for STEMI compared according to D1toB time <120 vs ≥120 minutes.
Fig. 3
The 4 individual processes of care for STEMI compared according to the urbanization levels (metropolitan, urban, and rural).
Abstract
Background
Interhospital transfer delays for ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients requiring primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) may be shortened by improved regional care systems. We evaluated the transfer process and first door-to-balloon (D1toB) time in STEMI patients who underwent interhospital transfer for primary PCI.
Methods and Results
We evaluated the D1toB time in 1837 patients who underwent interhospital transfer for primary PCI from the Cardiovascular Disease Surveillance program in Korea. Only 29.3% of patients had a D1toB time less than 120 minutes, as recommended by the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association guidelines for the management of STEMI. After adjusting for potential confounders, chest pain at presentation (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 2.06; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.18-3.83), transfer to a PCI center with an annual PCI volume greater than 200 (AOR, 1.35; 95% CI, 1.04-1.74), and higher urbanization level (AOR, 2.01 [95% CI, 1.40-2.91], for urban areas; AOR, 3.70 [95% CI, 2.59-3.83], for metropolitan areas) showed beneficial effects on reducing the D1toB time. The median length of stay in the referring hospital (D1LOS) and interhospital transport time were 50 (interquartile range [IQR], 30-100) minutes and 32 (IQR, 20-51) minutes, respectively. The median time interval from the door of the receiving hospital to balloon insertion was 55 (IQR, 40-79) minutes.
Conclusions
Patients with STEMI undergoing interhospital transfer did not receive definite care within the recommended therapeutic time window. Delays in the transfer process (length of stay in the referring hospital and interhospital transport time) were major contributors to the delay in the D1toB time.
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
☆Funding sources: This work was supported by Korean Center for Disease & Control.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..