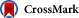Interaction of the diabetes mellitus and cardiac diseases on survival outcomes in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest☆☆☆
Affiliations
- Laboratory of Emergency Medical Services, Seoul National University Hospital Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Correspondence
- Corresponding author at: Department of Emergency Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, 101 Daehak-Ro, Jongno-Gu, Seoul 110-744, Korea. Tel.: +82 2 2072 3257; fax: +82 2 741 7855.

Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Correspondence
- Corresponding author at: Department of Emergency Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, 101 Daehak-Ro, Jongno-Gu, Seoul 110-744, Korea. Tel.: +82 2 2072 3257; fax: +82 2 741 7855.
Affiliations
- Laboratory of Emergency Medical Services, Seoul National University Hospital Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Affiliations
- Department of Emergency Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Affiliations
- Laboratory of Emergency Medical Services, Seoul National University Hospital Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Affiliations
- Department of Social Medicine, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, South Korea
Affiliations
- Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Chungbuk, South Korea
Affiliations
- Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Chungbuk, South Korea
Affiliations
- Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Chungbuk, South Korea
 Article Info
Article Info
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
Figure
Study population OHCA, out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
Abstract
Background
Diabetes mellitus (DM) and cardiac disease (CD) both likely effect out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) survival, but the effect of their relationship on survival outcomes is unclear. This study aims to investigate whether the association of DM and OHCA outcomes differ in patients with and without CD.
Methods
The study was conducted from the national cardiac arrest registry among OHCA patients who survived to hospital admission from 2009 to 2013. Clinical histories of DM and CD were abstracted from patient medical records. Multivariable logistic regression analysis with an interaction term (DM and CD) was performed to calculate adjusted odds ratios (AORs) for survival to discharge and good cerebral performance category 1 or 2 (good CPC).
Results
Among 7583 study-eligible patients, 2651 (34.96%) patients had been previously diagnosed as having DM where 639 (24.1%) diabetic and 753 (15.3%) nondiabetic patients had CD (P < .01). Diabetes mellitus was observed to have harmful effect on survival and good CPC (AORs, 0.84 [0.75-0.95] and 0.81 [0.67-0.97]), whereas CD had nonsignificant effect (AORs, 1.34 [1.17-1.54] and 1.14 [0.94-1.38]). Diabetes mellitus had a significant negative association with survival outcomes in patients with CD (AORs, 0.58 [0.45-0.74] for survival and 0.52 [0.36-0.75] for good CPC), whereas the association was nonsignificant in patients without CD (AORs, 0.93 [0.82-1.06] for survival and [0.76-1.14] for good CPC).
Conclusion
Diabetes mellitus had a significant negative association with survival to discharge and neurologic recovery among patients with CD, but the association was not significant in patients without CD.
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
☆Funding and conflict of interest: This study was supported by the National Emergency Management Agency of Korea and the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The study was funded by the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2009-2013). There are no conflicts of interest for all authors in this study.
☆☆Disclosure: None.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..