Effects of long axis in-plane vs short axis out-of-plane techniques during ultrasound-guided vascular access☆☆☆
Affiliations
- Department of Ultrasonography, Qilu Hospital, Shandong University, Jinan, 250000, Shandong, China
- Department of Ultrasonography, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou, 256603, China
Affiliations
- Department of Ultrasonography, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou, 256603, China
Affiliations
- Department of Spine Surgery, Binzhou People's Hospital, Binzhou, 256610, China
Affiliations
- Department of Ultrasonography, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou, 256603, China
Affiliations
- Department of Ultrasonography, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou, 256603, China
Affiliations
- Department of Ultrasonography, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou, 256603, China
Affiliations
- Department of Ultrasonography, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou, 256603, China
Affiliations
- Department of Ultrasonography, Qilu Hospital, Shandong University, Jinan, 250000, Shandong, China
Correspondence
- Corresponding author: Department of Ultrasonography, Qilu Hospital, Shandong University, No. 107 Wenhua Xi Road, Jinan, 250000, Shandong, China. Tel./fax: +86 531 82169114.

Affiliations
- Department of Ultrasonography, Qilu Hospital, Shandong University, Jinan, 250000, Shandong, China
Correspondence
- Corresponding author: Department of Ultrasonography, Qilu Hospital, Shandong University, No. 107 Wenhua Xi Road, Jinan, 250000, Shandong, China. Tel./fax: +86 531 82169114.
 Article Info
Article Info
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
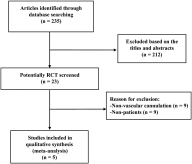
Fig. 1
Search strategy and flow chart of the meta-analysis.
Fig. 2
Risk-of-bias assessment. A, Risk-of-bias graph, the authors' judgments about each risk-of-bias item presented as percentages across all included studies. B, Risk-of-bias summary, the authors' judgments about each risk-of-bias item for the each included studies.
Fig. 3
Forest plot of the meta-analysis of RCTs. A, The first-pass success rate. B, Mean time to success. C, Mean attempts to success. D, Incidence of the complication of hematoma.
Abstract
Background
Currently, whether long-axis in-plane (LA-IP) is superior to short-axis out-of-plane (SA-OOP) during ultrasound-guided vascular access remains inconclusive. We, therefore, conducted a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials to compare the effects of LA-IP vs SA-OOP techniques in patients undergoing ultrasound-guided vascular access (USGVA).
Methods
A computer-based literature search of PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library (up to October 2015) was performed to identify randomized controlled trials that evaluated the effects of LA-IP compared with SA-OOP in patients undergoing USGVA. The primary end point was the first-pass success rate. Secondary end points included mean time to success, mean attempts to success, and incidence of the complication of hematoma. Weighted mean differences (WMDs) and relative risks (RRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated by random-effects model.
Results
Five eligible studies with a total of 470 patients satisfied the inclusion criteria. There was no significant difference for the first-pass success rate (RR, 1.06; 95% CI, 0.91-1.23; P = .44), mean time to success (WMD, 4.78 seconds; 95% CI, −4.43 to 13.99; P = .31), mean attempts to success (WMD, 0.06 times; 95% CI, −0.23 to 0.35; P = .69), and incidence of the complication of hematoma (RR, 2.86; 95% CI, 0.32-25.42; P = .35) between the LA-IP and SA-OOP groups.
Conclusions
There is insufficient evidence to definitively choose either LA-IP or SA-OOP in patients undergoing USGVA. Further robustly well-designed trials are warranted to investigate the appropriate technique in patients receiving USGVA.
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..