Novel technique in ED: supracondylar ultrasound-guided nerve block for reduction of distal radius fractures
Ali Attila Aydin

,,,,x
, MDAli Attila Aydin
Search for articles by this author
Correspondence
- Corresponding author at: Department of Emergency Medicine, Gulhane Military Medical Academy, Ankara, Turkey.

x
Ali Attila Aydin
Search for articles by this author
Correspondence
- Corresponding author at: Department of Emergency Medicine, Gulhane Military Medical Academy, Ankara, Turkey.
Department of Emergency Medicine, Gulhane Military Medical Academy, Ankara, Turkey
 Article Info
Article Info
Publication History
Published Online: February 12, 2016Accepted: February 2, 2016; Received in revised form: February 1, 2016; Received: January 22, 2016;
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
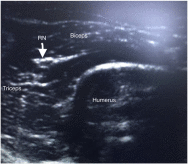
Fig. 1
Ultrasound-guided view of anatomical structures during procedure. Abbreviation: RN, radial nerve.
Fig. 2
Location of the supracondylar radial block puncture side.
Distal radius fractures (DRFs) of the wrist are the most common upper extremity fracture presented to an emergency department (ED). Distal radius fracture, requiring manipulation and reduction, is frequently encountered in the ED. Several methods have been used for pain management during the procedure. These include peripheral nerve block (PNB), hematoma block (HB), intravenous regional anesthesia (IVRA), procedural sedation analgesia (PSA), nitrous oxide and general anesthesia
[1]
. Ultrasound (US)–guided PNBs, performed by emergency physicians, have gradually gained a place in emergency practice.
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
© 2016 Elsevier Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Access this article on
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..