Article in Press
Comparison of two intravascular access techniques when using CBRN-PPE: A randomized crossover manikin trial☆
Lukasz Szarpak, PhD, EMT-P, DPH
, Zenon Truszewski

x
, PhD, MDZenon Truszewski
Search for articles by this author
Correspondence
- Corresponding author at: Department of Emergency Medicine, Medical University of Warsaw, Poland, 4 Lindleya Str., 02-005 Warsaw, Poland. Tel.: +48 502258562.

x
Zenon Truszewski
Search for articles by this author
Correspondence
- Corresponding author at: Department of Emergency Medicine, Medical University of Warsaw, Poland, 4 Lindleya Str., 02-005 Warsaw, Poland. Tel.: +48 502258562.
Department of Emergency Medicine, Medical University of Warsaw, Poland
Jacek Smereka, PhD, MD
Department of Emergency Medical Service, Wroclaw Medical University, Wroclaw, Poland
Marcin Madziała, MSc
Department of Emergency Medicine, Medical University of Warsaw, Poland
Lukasz Czyzewski, PhD, RN
Department of Nephrologic Nursing, Medical University of Warsaw, Warsaw, Poland
 Article Info
Article Info
Publication History
Published Online: March 21, 2016Accepted: March 17, 2016; Received: March 16, 2016;
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
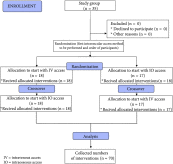
Figure
Flow chart of design and recruitment of participants according to CONSORT statement.
Rapid intravascular access is critical procedure in many emergency situations [1]. Gold standard of intravascular access in emergency scenarios it is still intravenous access. However, there are situations where intravenous (IV) access is difficult, or even impossible. Such situations can include hypovolemic shock or cardiac arrest, in which veins are collapsed [2]. Difficulties in access can also make use of personal protective equipment, including wearing chemical. Biological, radiological and nuclear (CBRN) protective equipment.
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
☆Source of support: No sources of financial and material support to be declare
© 2016 Elsevier Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Access this article on
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..


