Article in Press
Adropın levels and target organ damage secondary to Hıgh blood pressure in emergency department
Bedia Gulen

,x
, MDBedia Gulen
Search for articles by this author
Affiliations
- BezmialemVakifUniversity, Department of EmergencyMedicine, Istanbul, Turkey
Correspondence
- Corresponding author.

x
Bedia Gulen
Search for articles by this author
Affiliations
- BezmialemVakifUniversity, Department of EmergencyMedicine, Istanbul, Turkey
Correspondence
- Corresponding author.
Cenker Eken
,x
, MDCenker Eken
Search for articles by this author
Affiliations
- Akdeniz University, Department of EmergencyMedicine, Antalya, Turkey
Okkes Taha Kucukdagli
,x
, MDOkkes Taha Kucukdagli
Search for articles by this author
Affiliations
- BakirkoyDr.Sadi Konuk Training andResearchHospital, Istanbul, Turkey
Mustafa Serinken
,x
, MDMustafa Serinken
Search for articles by this author
Affiliations
- Pamukkale University, Department of EmergencyMedicine, Denizli, Turkey
Abdurrahim Kocyigit
,x
, MDAbdurrahim Kocyigit
Search for articles by this author
Affiliations
- BezmialemVakifUniversity, Department of Biochemistry, Istanbul, Turkey
Elif Kılıc
,x
, MDElif Kılıc
Search for articles by this author
Affiliations
- BezmialemVakifUniversity, Department of Biochemistry, Istanbul, Turkey
Hüseyin Uyarel
x
, MDHüseyin Uyarel
Search for articles by this author
Affiliations
- BezmialemVakifUniversity, Department of Cardiology, Istanbul, Turkey
 Article Info
Article Info
Publication History
Published Online: April 13, 2016Accepted: April 10, 2016; Received in revised form: April 8, 2016; Received: March 7, 2016;
To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription. Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect.
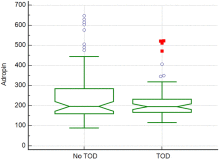
Fig. 1
TOD of the relation between serum adropin levels and blood pressure
Abbreviations: TOD: target organ disease.
Hypertension (HT) is the most important risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, and ranks 4th among the most frequently seen medical conditions. Nearly 75% of hypertensive USA population can not maintain their blood pressures at 140/90 mm Hg, and consequently many patients present to the emergency department (ED) because of high blood pressure. Most scaring complication of hypertension is hypertensive emergency which defined as large elevations in SBP or DBP (>180 mmHg or >120 mmHg, respectively) associated with impending or progressive OD, such as major neurological changes, hypertensive encephalopathy, cerebral infarction, intracranial haemorrhage, acute LV failure, acute pulmonary oedema, aortic dissection, renal failure, or eclampsia [1].
To access this article, please choose from the options below
Purchase access to this article
Claim Access
If you are a current subscriber with Society Membership or an Account Number, claim your access now.
Subscribe to this title
Purchase a subscription to gain access to this and all other articles in this journal.
Institutional Access
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
© 2016 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Access this article on
Visit ScienceDirect to see if you have access via your institution.
Related Articles
Searching for related articles..


